| | Organic Chemistry |  |
|
+4ahmed mansour sohair الباش مهندس عصايه هانم 8 مشترك |
| كاتب الموضوع | رسالة |
|---|
عصايه هانم
عالم مشهور





عدد الــمــساهـمــات : 2087
تاريخ الميلاد : 01/02/1992
العمر : 32
الفرقة : الثانية
القسم أو الشعبة : جيولوجيا
تاريخ التسجيل : 03/12/2009
الأوسمة : 
 |  موضوع: Organic Chemistry موضوع: Organic Chemistry  الخميس مايو 06, 2010 7:10 pm الخميس مايو 06, 2010 7:10 pm | |
|
المحاضرة الأولى
Hydrocarbons can be classified as
1. Alkanes
2. Alkenes
3. Alkynes
4. Aromatic Hydrocarbons
Alkanes (Paraffins): They contain single bonds. They are called saturated hydrocarbon. The first four are gases, next thirteen are gases and the higher are
solids. Their general molecular formula is CnH2n+2.
E.g. Methane (CH4), Ethane (C2H6), Propane (C3H8), Butane (C4H10), Pentane
o(C5H12) etc
Alkenes (Olefins): They contain at least one double bond. They are called unsaturated hydrocarbon. The first three are gases, next fourteen are liquids and higher are solids. Their general molecular formula is CnH2n.
E.g. Ethene (C2H4), Propene (C3H6), Butene (C4H8) etc
Alkynes: They contain one least one triple bond. They are called unsaturated hydrocarbon. The first three are gases, next eight are liquids and higher are solids. Their general molecular formula is CnH2n-2.
E.g. Ethyne (C2H2), Propyne (C3H4) etc
Aromatic Hydrocarbons (Arenes): They are planar, ring structures with alternating single and double bonds: E.g. Benzene (C6 H6), Toluene etc.
The Aromatic Hydrocarbons which contains benzene ring are called benzoids (cyclic) and the compounds which do not contain benzene rings are called non benzoids (acyclic).
ـــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــ
General chemical formulas
If a hydrocarbon molecule contains "n" carbon atoms, and the type of hydrocarbon is known, its general chemical formula can be written as follows:
Alkane: CnH2n+2. Cycloalkane: CnH2n (assuming a single ring, with all the carbon atoms in the ring structure). Alkene: CnH2n (assuming only one double bond in each molecule). Alkyne: CnH2n-2 (assuming only one triple bond in each molecule).
Aromatic ring: CnHn (assuming a single ring, with all the carbon atoms in the ring structure).
ــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــ Chemical Bonds Bonds between atoms :Ionic Bond : is a bond in which one or more electrons from one atom are removed and attached to another atom, resulting in positive and negative ions which attract each other.Metal + non metalFor example, When sodium (Na) and chlorine (Cl) are combined, the sodium atoms each lose an electron, forming a cation (Na+), and the chlorine atoms each gain an electron to form an anion (Cl−). These ions are then attracted to each other in a 1:1 ratio to form sodium chloride (NaCl).Na + Cl → Na+ + Cl− → NaClCovalent Bond : is a bond in which one or more pairs of electrons are shared by two atoms.Non metal + non metal
For example,
 Co-ordinate bond (also called a dative covalent bond) : is a covalent bond (a shared pair of electrons) in which both electrons come from the same atom.Lone pair donor atom + Lone pair acceptor atomFor example,
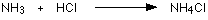 Ammonium ions, NH4+, are formed by the transfer of a hydrogen ion from the hydrogen chloride to the lone pair of electrons on the ammonia molecule.Bonds between molecules :Hydrogen Bond : A hydrogen bond is the attractive force between the hydrogen attached to an electronegative atom of one molecule and an electronegative atom of a different molecule.هنا ترتبط ذرة الهيدروجين مع ذرات أعلى منها فى السالبية الكهربية مثل : O - F - NDipole-Dipole attractions : Dipole-dipole forces are attractive forces between the positive end of one polar molecule and the negative end of another polar molecule. Ammonium ions, NH4+, are formed by the transfer of a hydrogen ion from the hydrogen chloride to the lone pair of electrons on the ammonia molecule.Bonds between molecules :Hydrogen Bond : A hydrogen bond is the attractive force between the hydrogen attached to an electronegative atom of one molecule and an electronegative atom of a different molecule.هنا ترتبط ذرة الهيدروجين مع ذرات أعلى منها فى السالبية الكهربية مثل : O - F - NDipole-Dipole attractions : Dipole-dipole forces are attractive forces between the positive end of one polar molecule and the negative end of another polar molecule.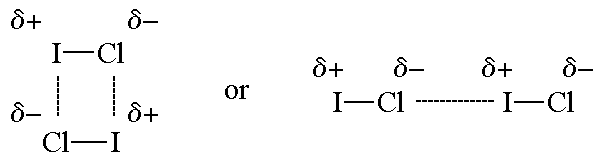 Van der Wal's forces : are the attractive or repulsive forces between molecules (or between parts of the same molecule) oو ينتج نتيجة للتوزيع الغير متماثل للالكتورنات حول النواةInclusion forces :Guest + HostExample, Starch+Iodin solution >>>> Blue colour Van der Wal's forces : are the attractive or repulsive forces between molecules (or between parts of the same molecule) oو ينتج نتيجة للتوزيع الغير متماثل للالكتورنات حول النواةInclusion forces :Guest + HostExample, Starch+Iodin solution >>>> Blue colour
Arrangement of Bonds according to strength
Ionic Bond
Covalent Bond
Co-ordinate Bond
Hydrogen Bond
Dipole-Dipole Forces
Van der Wal's Forces
| |
|
  | |
عصايه هانم
عالم مشهور





عدد الــمــساهـمــات : 2087
تاريخ الميلاد : 01/02/1992
العمر : 32
الفرقة : الثانية
القسم أو الشعبة : جيولوجيا
تاريخ التسجيل : 03/12/2009
الأوسمة : 
 |  موضوع: رد: Organic Chemistry موضوع: رد: Organic Chemistry  الخميس مايو 06, 2010 7:33 pm الخميس مايو 06, 2010 7:33 pm | |
| | |
|
  | |
الباش مهندس
الدعـــم الـفـــنــّى
و مراقب المشرفين





عدد الــمــساهـمــات : 2229
تاريخ الميلاد : 12/12/1989
العمر : 34
العمل/الترفيه : طالب بهندسة شبرا
الفرقة : غير ذلك
القسم أو الشعبة : غير ذلك
تاريخ التسجيل : 19/06/2008
الأوسمة : 

 | |
  | |
sohair
عالم مشهور





عدد الــمــساهـمــات : 1130
تاريخ الميلاد : 17/06/1991
العمر : 33
العمل/الترفيه : طالبه
الفرقة : الأولى
القسم أو الشعبة : غير ذلك
تاريخ التسجيل : 11/03/2010
 |  موضوع: رد: Organic Chemistry موضوع: رد: Organic Chemistry  الخميس مايو 06, 2010 9:40 pm الخميس مايو 06, 2010 9:40 pm | |
| تسلم ايدك
يا عصايه على المجهود | |
|
  | |
ahmed mansour
عالم مشهور





عدد الــمــساهـمــات : 597
تاريخ الميلاد : 02/10/1991
العمر : 33
العمل/الترفيه : طالب/ممثل
الفرقة : الأولى
القسم أو الشعبة : علوم الارض
تاريخ التسجيل : 24/01/2009
الأوسمة : 

 |  موضوع: رد: Organic Chemistry موضوع: رد: Organic Chemistry  الجمعة مايو 07, 2010 3:15 am الجمعة مايو 07, 2010 3:15 am | |
| | |
|
  | |
basma
عالم بيفكر





عدد الــمــساهـمــات : 248
تاريخ الميلاد : 05/05/1992
العمر : 32
الفرقة : الأولى
القسم أو الشعبة : فيزيائية
تاريخ التسجيل : 25/11/2009
 |  موضوع: رد: Organic Chemistry موضوع: رد: Organic Chemistry  الجمعة مايو 07, 2010 10:28 am الجمعة مايو 07, 2010 10:28 am | |
| بجد ربنا يكرمك
كنت محتجاها اوى | |
|
  | |
عصايه هانم
عالم مشهور





عدد الــمــساهـمــات : 2087
تاريخ الميلاد : 01/02/1992
العمر : 32
الفرقة : الثانية
القسم أو الشعبة : جيولوجيا
تاريخ التسجيل : 03/12/2009
الأوسمة : 
 |  موضوع: رد: Organic Chemistry موضوع: رد: Organic Chemistry  الجمعة مايو 07, 2010 5:56 pm الجمعة مايو 07, 2010 5:56 pm | |
|
المحاضرة الثانية
Determation of Empirical & Molecular formula
تعيين الصيغة الأولية و الصيغة الثانوية
Empirical formula:o
هى أبسط صيغة قد تعبر عن النسبة بين العناصر بعضها البعض و قد لا تعبر عن العدد الحقيقى لذرات العنصر فى الجزىء .
طريقة التعيين :
(1) تعين النسبة المئوية للعناصر المختلفة التى تدخل فى تركيب المادة فاذا كان مجموع هذه النسب أقل من مائة , دل هذا ع أن المادة تشتمل على الأكسجين و الفرق هو نسبة الأكسجين فى المادة .
(2) تقسم النسبة المئوية لكل عنصر على وزنها الذرى
(3) تنسب الأرقام الناتجة من العملية السابقة الى أصغرها لمعرفة نسبة العناصر بعضها الى بعض اذا كانت الأعداد النسبية كسورا يتم ضربها فى أصغر عدد صحيح للحصول على الصيغة الأولية مع إهمال الكسور الصغيرة جدا ..
ــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــــ
القوانين :
Molecular formula = (Empirical formula)n
n = Molecular weight / Emperical formula weight
Molecular weight = 2 x density
لحساب نسبة الأكسجين :
نجمع كل النسب و نطرحهم من 100
لو جت مسألة غير مباشرة و عاوز الصيغة الأولية أو الصيغة الثانوية و هو مش جايب نسب أساسا ف المسألة :
مثال :
An 0.45 gm of organic acid Give 0.44 gm of Co2 after burning
الحل :
C % in Co2 = 12/44 x 0.44/0.45 x 100 = 26.66%
حيث 12 هو الوزن الذرى لعنصر الكربون , 44 هو كتلة المول من Co2 حيث :
كتلة المول = (12+2*16)ه
وحيث 0.44 هو كتلة الكربون فى الحمض و 0.45 هى كتلة الحمض نفسه
| |
|
  | |
glade
عالم مشهور





عدد الــمــساهـمــات : 880
تاريخ الميلاد : 27/09/1992
العمر : 32
الفرقة : الأولى
القسم أو الشعبة : فيزيائية
تاريخ التسجيل : 13/10/2009
الأوسمة : 
 |  موضوع: رد: Organic Chemistry موضوع: رد: Organic Chemistry  الجمعة مايو 07, 2010 7:06 pm الجمعة مايو 07, 2010 7:06 pm | |
| | |
|
  | |
alyoyo
عالم شغال




عدد الــمــساهـمــات : 72
تاريخ الميلاد : 14/03/1993
العمر : 31
الفرقة : الأولى
القسم أو الشعبة : غير ذلك
تاريخ التسجيل : 15/03/2010
 |  موضوع: رد: Organic Chemistry موضوع: رد: Organic Chemistry  الجمعة مايو 07, 2010 7:45 pm الجمعة مايو 07, 2010 7:45 pm | |
| مجهود رائع جدا يا عصاية
شكرا جزيلا ويا ريت تكملى
بقى باقى المحاضرات | |
|
  | |
الباش مهندس
الدعـــم الـفـــنــّى
و مراقب المشرفين





عدد الــمــساهـمــات : 2229
تاريخ الميلاد : 12/12/1989
العمر : 34
العمل/الترفيه : طالب بهندسة شبرا
الفرقة : غير ذلك
القسم أو الشعبة : غير ذلك
تاريخ التسجيل : 19/06/2008
الأوسمة : 

 | |
  | |
عصايه هانم
عالم مشهور





عدد الــمــساهـمــات : 2087
تاريخ الميلاد : 01/02/1992
العمر : 32
الفرقة : الثانية
القسم أو الشعبة : جيولوجيا
تاريخ التسجيل : 03/12/2009
الأوسمة : 
 |  موضوع: رد: Organic Chemistry موضوع: رد: Organic Chemistry  الجمعة مايو 07, 2010 11:46 pm الجمعة مايو 07, 2010 11:46 pm | |
| المحاضرة الثالثة
nomenclature of organic compounds
The steps to naming an organic compound are:
Identify the parent hydrocarbon chain (The longest continuous chain of carbon atoms) Identify the functional group, if any (If more than one, use the one with highest precedence as shown down here)
No | group | Prefix name | Suffix name | 1 | COOH- | carboxy | oic acid- | 2 | COOR- | Alkoxy carbonyl | Alkyl carboxylate | 3 | SO3H- | sulpho | Sulphonic acid | 4 | COX- | Halo formyl | oyl halide- | 5 | CONH2 | carbamyl | o amide- | 6 | CHO- | formyl | al- | 7 | CN- | cyano | nitrile | 8 | C=O | keto | one- | 9 | OH- | hydroxy | ol- | 10 | SH- | mercapto | thiol- | 11 | NH= | amine | amine | 12 | C=C | ـــــــــــــــ | ene | 13 | C --- C | ـــــــــــــــ | yne | 14 | –O– | epoxy | ـــــــــــــــ | 15 | N=N | azo | ـــــــــــــــ | 16 | NO2- | nitro | ـــــــــــــــ | 17 | NO | nitroso | ـــــــــــــــ |
Identify the position of the functional group in the chain. Number the carbon atoms in the parent chain. The functional group should end up the least number possible (as there are two ways of numbering—right to left and left to right). The number (i.e. 1, 2, 3....) is written before the name of the functional group suffix (such as -ol, -one, -al, etc.). If the group is a group that can only exist at the end of any given chain (such as the carboxylic acid and aldehyde groups), it need not be numbered.
NOTE: If there are no functional groups, number in both directions, find the numbers of the side-chains (the carbon chains that are not in the parent chain) in both directions. The end result should be such that the first number should be the least possible. In the event of the first numbers being the same for two methods of numbering, the sum of the numbers of the side chains should be made the least possible; for example, 2,2,5-trimethylhexane (2 + 2 + 5 = 9) is preferred over 2,5,5-trimethylhexane (2 + 5 + 5 = 12), as they both start with '2', but the sum of the numbers of the former is less.
Identify the side-chains and number them. Side chains are the carbon chains that are not in the parent chain, but are branched off from it.
If there is more than one of the same type of side-chain, add the prefix (di-, tri-, etc.) before it. The numbers for that type of side chain will be grouped in ascending order and written before the name of the side-chain. If there are two side-chains with the same alpha carbon, the number will be written twice. Example: 2,2,3-trimethyl... Identify the remaining functional groups, if any, and name them by the name of their ions (such as hydroxy for -OH, oxy for =O , oxyalkane for O-R, etc.).
Different side-chains and functional groups will be grouped together in alphabetical order. (The prefixes di-, tri-, etc. are not taken into consideration for grouping alphabetically. For example, ethyl comes before dihydroxy or dimethyl, as the "e" in "ethyl" precedes the "h" in "dihydroxy" and the "m" in "dimethyl" alphabetically. The "di" is not considered in either case). In the case of there being both side chains and secondary functional groups, they should be written mixed together in one group rather than in two separate groups. Identify double/triple bonds. Number them with the number of the carbon atom at the head of the bond (i.e. the carbon atom with the lesser number that it is attached to). For example a double bond between carbon atoms 3 and 4 is numbered as 3-ene. Multiple bonds of one type (double/triple) are named with a prefix (di-, tri-, etc.). If both types of bonds exist, then use "ene" before "yne" e.g. "6 13 diene 19 yne". If all bonds are single, use "ane" without any numbers or prefixes. Arrange everything like this: Group of side chains and secondary functional groups with numbers made in step 3 + prefix of parent hydrocarbon chain (eth, meth) + double/triple bonds with numbers (or "ane") + primary functional group suffix with numbers.
Wherever it says "with numbers", it is understood that between the word and the numbers, you use the prefix(di-, tri-) Add punctuation:
Put commas between numbers (2 5 5 becomes 2,5,5) Put a hyphen between a number and a letter (2 5 5 trimethylhexane becomes 2,5,5-trimethylhexane) Successive words are merged into one word (trimethyl hexane becomes trimethylhexane)
NOTE: IUPAC uses one-word names throughout. This is why all parts are connected.
</LI>
عدل سابقا من قبل عصايه هانم في الجمعة مايو 07, 2010 11:58 pm عدل 1 مرات | |
|
  | |
sohair
عالم مشهور





عدد الــمــساهـمــات : 1130
تاريخ الميلاد : 17/06/1991
العمر : 33
العمل/الترفيه : طالبه
الفرقة : الأولى
القسم أو الشعبة : غير ذلك
تاريخ التسجيل : 11/03/2010
 |  موضوع: رد: Organic Chemistry موضوع: رد: Organic Chemistry  الجمعة مايو 07, 2010 11:52 pm الجمعة مايو 07, 2010 11:52 pm | |
| | |
|
  | |
Geo_MiDo
عالم مشهور





عدد الــمــساهـمــات : 433
تاريخ الميلاد : 20/02/1993
العمر : 31
الفرقة : الأولى
القسم أو الشعبة : علوم الارض
تاريخ التسجيل : 23/01/2010
 |  موضوع: رد: Organic Chemistry موضوع: رد: Organic Chemistry  الإثنين مايو 10, 2010 1:40 am الإثنين مايو 10, 2010 1:40 am | |
| | |
|
  | |
عصايه هانم
عالم مشهور





عدد الــمــساهـمــات : 2087
تاريخ الميلاد : 01/02/1992
العمر : 32
الفرقة : الثانية
القسم أو الشعبة : جيولوجيا
تاريخ التسجيل : 03/12/2009
الأوسمة : 
 |  موضوع: رد: Organic Chemistry موضوع: رد: Organic Chemistry  الجمعة مايو 14, 2010 2:57 am الجمعة مايو 14, 2010 2:57 am | |
| المحاضرة الرابعةIsomerism Isomers are molecules that have the same molecular formula, but have a different arrangement of the atoms in space. That excludes any different arrangements which are simply due to the molecule rotating as a whole, or rotating about particular bonds.For example, both of the following are the same molecule. They are not isomers. Both are butane. There are also endless other possible ways that this molecule could twist itself. There is completely free rotation around all the carbon-carbon single bonds.Structural IsomerismTypes of structural isomerismChain isomerismThese isomers arise because of the possibility of branching in carbon chains. For example, there are two isomers of butane, C4H10. In one of them, the carbon atoms lie in a "straight chain" whereas in the other the chain is branched. There are also endless other possible ways that this molecule could twist itself. There is completely free rotation around all the carbon-carbon single bonds.Structural IsomerismTypes of structural isomerismChain isomerismThese isomers arise because of the possibility of branching in carbon chains. For example, there are two isomers of butane, C4H10. In one of them, the carbon atoms lie in a "straight chain" whereas in the other the chain is branched. examplePentane, C5H12, has three chain isomers. If you think you can find any others, they are simply twisted versions of the ones below. If in doubt make some models. examplePentane, C5H12, has three chain isomers. If you think you can find any others, they are simply twisted versions of the ones below. If in doubt make some models. Position isomerismIn position isomerism, the basic carbon skeleton remains unchanged, but important groups are moved around on that skeleton.For example, there are two structural isomers with the molecular formula C3H7Br. In one of them the bromine atom is on the end of the chain, whereas in the other it's attached in the middle. Position isomerismIn position isomerism, the basic carbon skeleton remains unchanged, but important groups are moved around on that skeleton.For example, there are two structural isomers with the molecular formula C3H7Br. In one of them the bromine atom is on the end of the chain, whereas in the other it's attached in the middle. Another similar example occurs in alcohols such as C4H9OH Another similar example occurs in alcohols such as C4H9OH These are the only two possibilities provided you keep to a four carbon chain, but there is no reason why you should do that. You can easily have a mixture of chain isomerism and position isomerism - you aren't restricted to one or the other.So two other isomers of butanol are: These are the only two possibilities provided you keep to a four carbon chain, but there is no reason why you should do that. You can easily have a mixture of chain isomerism and position isomerism - you aren't restricted to one or the other.So two other isomers of butanol are: You can also get position isomers on benzene rings. Consider the molecular formula C7H8Cl. There are four different isomers you could make depending on the position of the chlorine atom. In one case it is attached to the side-group carbon atom, and then there are three other possible positions it could have around the ring - next to the CH3 group, next-but-one to the CH3 group, or opposite the CH3 group. You can also get position isomers on benzene rings. Consider the molecular formula C7H8Cl. There are four different isomers you could make depending on the position of the chlorine atom. In one case it is attached to the side-group carbon atom, and then there are three other possible positions it could have around the ring - next to the CH3 group, next-but-one to the CH3 group, or opposite the CH3 group. Functional group isomerism
In this variety of structural isomerism, the isomers contain different functional groups - that is, they belong to different families of compounds (different homologous series).
For example, a molecular formula C3H6O could be either propanal (an aldehyde) or propanone (a ketone).
There are other possibilities as well for this same molecular formula - for example, you could have a carbon-carbon double bond (an alkene) and an -OH group (an alcohol) in the same molecule.
Another common example is illustrated by the molecular formula C3H6O2. Amongst the several structural isomers of this are propanoic acid (a carboxylic acid) and methyl ethanoate (an ester). | |
Stereo IsomerismTypes of Stereo Isomerism Geommetrical - Optical Geommetrical Isomerism ( Restricted to alkenes =)i{all groups are attached to unsaturated carbons}  أنواعه : Cis - Trans فى ال Cis تتشابه العناصر اللى ف الجزء اللى فوق معًا كما تتشابه العناصر اللى تحت معًافى الTrans يكون هناك اختلاف ف العناصر ف الجزء اللى فوق .. كما يوجد اختلاف ف العناصر ف الجزء الأسفل أنواعه : Cis - Trans فى ال Cis تتشابه العناصر اللى ف الجزء اللى فوق معًا كما تتشابه العناصر اللى تحت معًافى الTrans يكون هناك اختلاف ف العناصر ف الجزء اللى فوق .. كما يوجد اختلاف ف العناصر ف الجزء الأسفل | |
|
  | |
عصايه هانم
عالم مشهور





عدد الــمــساهـمــات : 2087
تاريخ الميلاد : 01/02/1992
العمر : 32
الفرقة : الثانية
القسم أو الشعبة : جيولوجيا
تاريخ التسجيل : 03/12/2009
الأوسمة : 
 |  موضوع: رد: Organic Chemistry موضوع: رد: Organic Chemistry  الجمعة مايو 14, 2010 4:00 am الجمعة مايو 14, 2010 4:00 am | |
| | |
|
  | |
glade
عالم مشهور





عدد الــمــساهـمــات : 880
تاريخ الميلاد : 27/09/1992
العمر : 32
الفرقة : الأولى
القسم أو الشعبة : فيزيائية
تاريخ التسجيل : 13/10/2009
الأوسمة : 
 |  موضوع: رد: Organic Chemistry موضوع: رد: Organic Chemistry  الجمعة مايو 14, 2010 10:13 am الجمعة مايو 14, 2010 10:13 am | |
| | |
|
  | |
Geo_MiDo
عالم مشهور





عدد الــمــساهـمــات : 433
تاريخ الميلاد : 20/02/1993
العمر : 31
الفرقة : الأولى
القسم أو الشعبة : علوم الارض
تاريخ التسجيل : 23/01/2010
 | |
  | |
sohair
عالم مشهور





عدد الــمــساهـمــات : 1130
تاريخ الميلاد : 17/06/1991
العمر : 33
العمل/الترفيه : طالبه
الفرقة : الأولى
القسم أو الشعبة : غير ذلك
تاريخ التسجيل : 11/03/2010
 |  موضوع: رد: Organic Chemistry موضوع: رد: Organic Chemistry  الخميس مايو 27, 2010 8:33 pm الخميس مايو 27, 2010 8:33 pm | |
| | |
|
  | |
عصايه هانم
عالم مشهور





عدد الــمــساهـمــات : 2087
تاريخ الميلاد : 01/02/1992
العمر : 32
الفرقة : الثانية
القسم أو الشعبة : جيولوجيا
تاريخ التسجيل : 03/12/2009
الأوسمة : 
 | |
  | |
زائر
زائر
 | |
  | |
glade
عالم مشهور





عدد الــمــساهـمــات : 880
تاريخ الميلاد : 27/09/1992
العمر : 32
الفرقة : الأولى
القسم أو الشعبة : فيزيائية
تاريخ التسجيل : 13/10/2009
الأوسمة : 
 |  موضوع: رد: Organic Chemistry موضوع: رد: Organic Chemistry  الإثنين مايو 31, 2010 11:31 pm الإثنين مايو 31, 2010 11:31 pm | |
| بأذن الله عصاية وربنا مع كل بيولوجي في امتحان بكره ان شاء الله  | |
|
  | |
عصايه هانم
عالم مشهور





عدد الــمــساهـمــات : 2087
تاريخ الميلاد : 01/02/1992
العمر : 32
الفرقة : الثانية
القسم أو الشعبة : جيولوجيا
تاريخ التسجيل : 03/12/2009
الأوسمة : 
 | |
  | |
glade
عالم مشهور





عدد الــمــساهـمــات : 880
تاريخ الميلاد : 27/09/1992
العمر : 32
الفرقة : الأولى
القسم أو الشعبة : فيزيائية
تاريخ التسجيل : 13/10/2009
الأوسمة : 
 | |
  | |
عصايه هانم
عالم مشهور





عدد الــمــساهـمــات : 2087
تاريخ الميلاد : 01/02/1992
العمر : 32
الفرقة : الثانية
القسم أو الشعبة : جيولوجيا
تاريخ التسجيل : 03/12/2009
الأوسمة : 
 | |
  | |
| | Organic Chemistry |  |
|
